As Interventional Radiology and Oncology advances, robotic assistance becomes more and more valuable inside the operating rooms (ORs).
From improving surgical accuracy to lowering complication rates and radiation exposure, medical robots have been truly impacting clinical procedures and patient outcomes.
But there are many other challenges inside the ORs that only a full-fledged robotic system like Micromate™ can solve.
Micromate™: Bringing Versatility to the Operating Room
Micromate™’s versatility is one of the most valuable features that a medical robot could offer.
By seamlessly integrating into the already established clinical workflow, Micromate™’s live-imaging capabilities and 360º access make it the most advantageous tool for medical teams.
Besides, its portability makes it easy to transport between rooms since the whole system fits in a mobile cart, allowing more departments to use the robot in different types of procedures and locations of the body.
A Miniature Robotic System for Head-to-Toe Interventions
With Micromate™’s ability to reach challenging anatomical regions, procedures that were once considered too delicate and complex can now be conducted with enhanced accuracy and reduced risks.
Acting as a third hand, the system enables physicians to insert the instruments with finer and steadier movements, reaching complex anatomical structures without deviations.
Check out some examples of real, successful cases performed by physicians currently using Micromate™ in percutaneous procedures from head to toe:
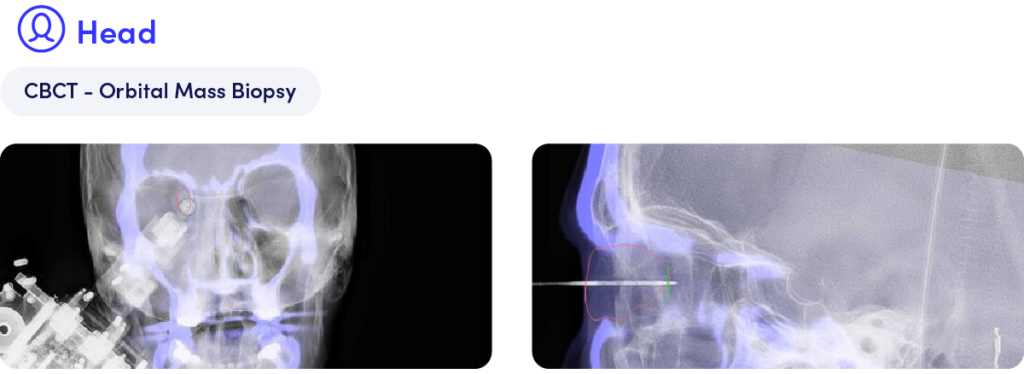
After imaging revealed a tumor in the orbital wall and sinuses of the patient, Micromate™ provided the stable needle guidance needed to help perform a safe biopsy in this sensitive area without damaging any critical structures nearby.
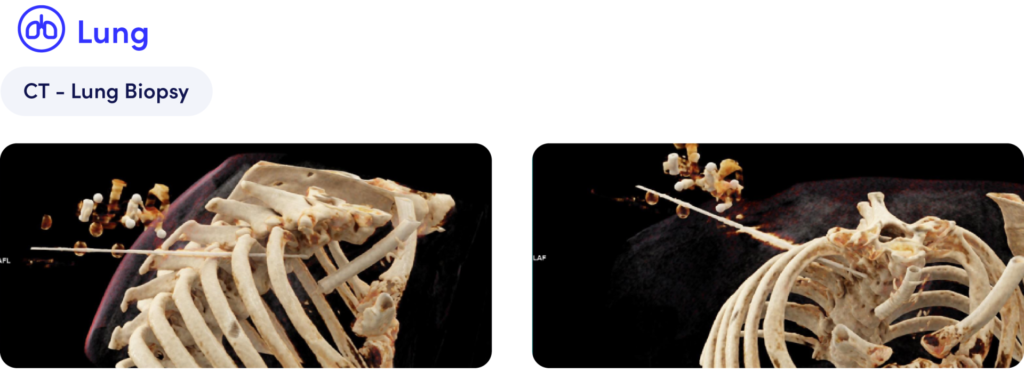
Thanks to its navigation and guidance features, our full-fledged robotic platform successfully assisted in performing a challenging lung biopsy – paravertebral through the narrow intercostal space – by accurately guiding the planning and execution of the procedure.
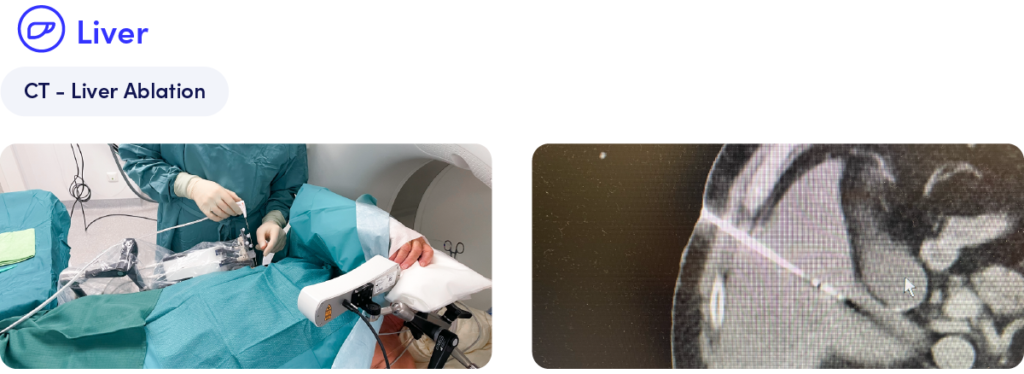
In this case, Micromate™ was used to accurately position the ablation probe at an oblique angle during a liver ablation procedure. With the robot’s intuitive needle trajectory planning capabilities, the instrument was guided with stability, making it possible to successfully reach a challenging target in a shorter time compared to the conventional workflow.

A bone biopsy of the iliac crest was performed with Micromate™ after several abnormal bone lesions were identified in a patient. Multiple needles were inserted within the range of motion of the robot, without the need to manually reposition the system, allowing the team to accurately reach the desired target.
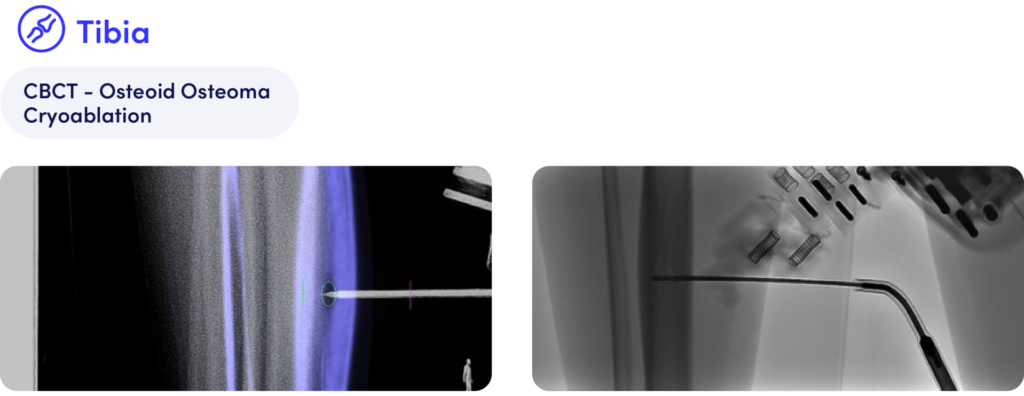
With the assistance of Micromate™, a patient with an osteoid osteoma in the right ventral tibia underwent a successful cryoablation where instrument access and alignment stability would be challenging if performed freehand.
Thanks to Micromate™‘s features, physicians have been able to successfully perform multiple percutaneous interventions from head to toe with the highest accuracy.
Its low footprint, 360º access, reduced invasiveness, compatibility with any instrument and most imaging modalities, and, above all, ability to reach challenging anatomical regions, have been playing a key role in significantly improving clinical outcomes.