Micromate™ Case Report series presents real cases performed by the physicians currently using our full-fledged robotic platform for percutaneous procedures.
For this case report, we join Dr. Alexander Kupferthaler, Interventional Radiologist at Ordensklinikum Linz – Barmherzige Schwestern, for a CT-guided lung biopsy.
Clinical Context
The patient was a 58-year-old male diagnosed with solitary plasma cell myeloma in 2018, with recurrence in 2023 with a lung lesion in the right lung apex paravertebral.
A biopsy was needed for treatment planning and genetic analysis.
Interventional Procedure
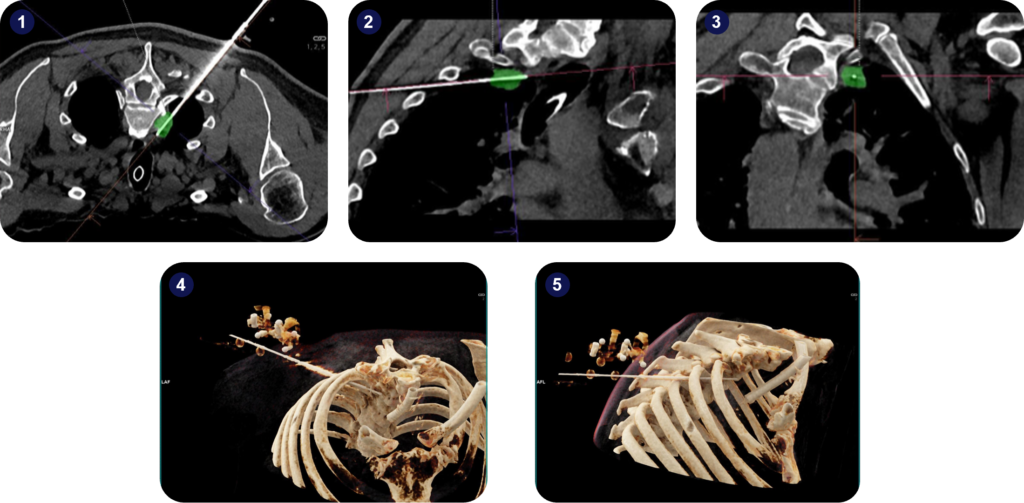
The patient was under general anesthesia with disconnection of the tube for breath-hold when scanning, needle puncture, and needle advancement.
The lesion size was 1.6×1.9 cm, and the trajectory path to the target was around 14 cm.
After automatic registration of the robot and planning, a 17G coaxial needle was advanced to the target. The correct position was confirmed with a single control scan at the target.
Next, an 18G biopsy needle was advanced through the middle of the lesion, and the specimen was taken. The last step was to remove the coaxial needle. The biopsy yielded accurate sampling, and recurrence was confirmed.
A non-significant pneumothorax, 5 mm, was visible on the postprocedural scan, but no additional treatment steps were required.
Key Takeaways
Micromate™ enabled the extraction of a biopsy from a challenging lesion – paravertebral through the narrow intercostal space. The robot’s navigation and guidance features facilitated the planning and execution process.
The system provided the clinical team with ease of use, accuracy, and the ability to perform challenging approaches.